EDU 807 Spring 2018 - Week 2 - Triple E Framework Group 3
Triple E Framework
About the Triple E Framework
Created by Dr. Liz Kolb, University of Michigan
http://www.tripleeframework.com/
|
What is the Triple E? The Triple E Framework attempts to define what it should look like, sound like and feel like to integrate technology tools into teaching in order to meet and exceed learning goals. The framework is based on three levels, Engagement in learning goals, Enhancementof learning goals, and Extension of learning goals. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are distinct and different. The Triple E Framework defines each term and show examples of what makes each one unique and measurable.
The Triple E Framework is based on a considerable amount of research about what works and does not work when it comes to technology in learning. In particular it emphasizes...
Read more about the research and links here
The Triple E Framework was developed in 2011 by Professor Liz Kolb at the University of Michigan, School of Education. The Triple E was created to fill a gap that has been pervasive in educational technologies---How to effectively integrate technology tools in K-12 learning so they have a positive impact on student achievement and learning outcomes.
WHY Triple E? The research on technology and learning over the past decade is fairly clear, technology should be integrated based on what we already know about good teaching and pedagogical practices. Dating back to the late 19th century, the foundation of current teaching practices is based on the work of pragmatism. Pragmatists like John Dewey (1897) pushed for learning to be embedded in the student's authentic everyday lives, socially constructed knowledge, active/hands-on learning and full of choice. Since the early 1990s Research has found that educational technology with a "drill and practice" approach often has no effects on learning or cognition. Yet, most technology tools created for education are still drill and practice and in the lower-order of Blooms Taxonomy.
Despite media often claiming a new piece of technology as a way to "revolutionize" learning, that is almost never the case. The Triple E framework takes this fallacy of technology as the magic bullet learning into account, and allows teachers to become critical consumers of making mindful choices around technology tools in their teaching. It is a simple framework, based on research, that helps educators create lessons that allow students to use technology to meet and add value to learning goals as active, social, creative learners, in authentic ways.
How Triple E is Different than other Tech Integration Models
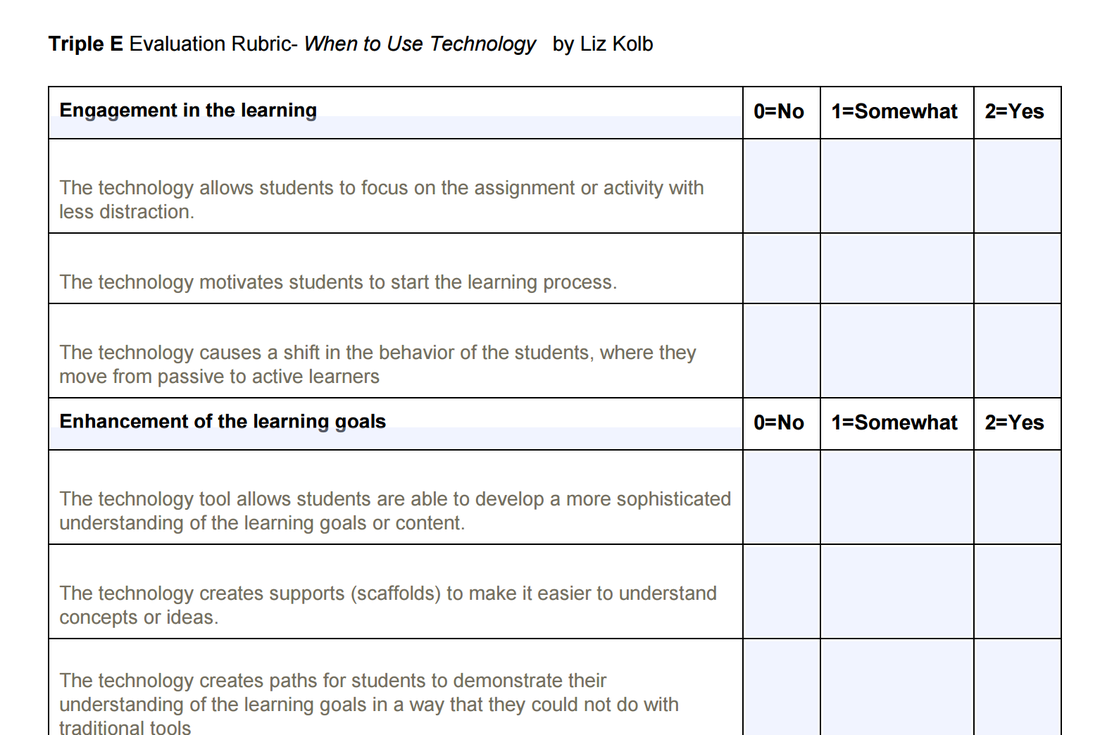
Triple E Level 1: Engaged Learning
|









0 General Document comments
0 Sentence and Paragraph comments
0 Image and Video comments
I thought this whole section from paragraph 12-22 rather than calling these areas of emphasis really is reiterating, or developing if you will a list of principles for the effective application of technology in learning. These principles are the basis of what they have come to value (the three E’s) and use as criteria to judge the effectiveness of the application of technology to teaching. It’s very interesting, they could have written this much like the Agile Manifesto and said we value Extension, Enhancement, and Engagement and the principles that underlie these values are para 12-22.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
I agree with you Jeff, these are good criteria to determine the effectiveness of applying technology to learning. This would be a good topic or checklist for a professional development session.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
This is an interesting paragraph and I find the concept of authentic learning combined with technolgy and problem based learning to be very interesting and IMHO possibly a great way to effectively incorporate technology. PBL may be advanced for K-12, I am not in that field but conceptually I think this is a good mix to gain the most with technology.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
I actually like this assumption, that 21st century educators are less likely to assume that the technology is going to go into full AI mode and teach the class for us or perform miracles. This reminds me of the Clark vs. Kozma debate we returned to several times in EDU800: the question of whether technology actually impacts learning or not. This assumption seems to fall into the Clark camp, which is that media doesn’t actually influence learning directly.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
Very curious to hear more of your thinking on this.
Did Clark argue that media didn’t influence learning directly, or that it didn’t influence learning at all?
I’ve got to get my hands on that article from Mike!
At any rate, I’m curious because I think that the way we talk about the hardware/device/tool – as well as the content/media – matters a great deal. Devices, offer my perspective, only offer us opportunities to engage in different types of media. Whether we are passive consumers, semi-active consumers, or producers makes a big difference in what happens for learning. Just curious to hear more of your thoughts on that.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
Here is a quote from the article we read:
My early articles (Clark, 1983, 1985a) claimed, in part, that media are “mere vehicles that deliver instruction but do not influence student achievement any more than the truck that delivers our groceries causes changes in our nutrition” (1983, p. 445)
Clark, R. E. (1983). Media will never influence learning. Educational Technology Research and Development, 42(2), 21-29.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
I thought this paragraph to be important in this concept and one that I largely agree with. Technology is a “Tool”. I find myself remaining in the Clark camp. I find technology to be just medium or media to deliver content. Technology impacts learning when it is integrated into a learning environment through appropriate application of learning theories, instructional strategies and instructional design. So, if you applied a Constructivist approach (theory) with Authentic Learning Strategies and PBL Strategies into a course design for a Blended Learning, Civil Engineering: Road Construction class, the technology doesn’t teach it just facilitates the learning because integrated correctly groups can work on problems together, their are multiple methods for providing feedback etc. Technology greatly enhances the capability to deliver learning but doesn’t change learning (My next statement will be the most controversial largely because the wording will be imprecise) because, Learning is something that happens within an individual. The mechanism of delivery be it a lecture or a webinar is just a delivery mechanism.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
In Cuban’s article, the Technophiles scenario stated: “students will come to rely on the machines and one another to teach them and teachers will become coaches to help students with what needs to be learned” (paragraph #53). I think this framework assumes the Technophiles’ statement to be true, that all students will someday have technology in their hands.
This framework assumes that all students embrace technology which is not true. Some students do not have adequate access to technology beyond school and have not been exposed to its potential by their families or communities. Technology can be intimidating to these students because they may feel “behind” their peers in how to functionally use it.
I think this framework also generalizes technology and assumes that any form of it will spark interest or engagement with students. Personally, I know my son in high school is not thrilled at all with his Chromebook because of the computer he uses at home (which he built himself). His generation grew up with the most sophisticated technological devices and most schools (I assume) are not utilizing cutting edge software and technology tools.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
Thanks, Pamela, for making the point that not all students immediately embrace technology and become “engaged.” To that point, I think you’re actually building on Kolb’s idea here…
I think that her concern is that many teachers go to the “default mode” of saying that technology is “engaging” and that is one of their first reasons for using it. It shouldn’t be. Moreover, as you point out with your son, if the technology itself is insufficient, then that could cause students to become unengaged as well.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
I’m glad the author pointed out the “bells and whistles” effect. I know I read a study last semester that indicated that new technology did increase student engagement by simple virtue of being new, but that effect wore off quickly, and perhaps even had a negative effect in the long run. The author here builds in the assumption that the bells and whistles effect will indeed wear off, and only at that point can effectiveness of technology be truly determined.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
I think this framework assumes that teachers will be able to effectively create a lesson plan that integrates technology to aid or bring value-added enhancement. It assumes the teacher will know what areas of the lesson to incorporate technology tools (substitute a traditional method with technology). It seems to me this framework in itself is a good professional development topic.
The framework also assumes that teachers already know how to use various software and tech tools well enough to provide students with a software/technology tour to meet learning goals (as in the Dog Sleds case study in paragraph #10).
Another assumption is that teachers will know and understand which technology tool is best to use to enhance learning. How would a teacher know this if the district didn’t offer professional development? A conference? Seeking information on their own?
Lastly, I think the framework assumes that teachers will be able to effectively model how to use the technology to enhance learning. To me, if their teaching skills were not great before the introduction of technology, the integration of the new tool will not dramatically change their teaching style, skills, and performance.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
The professional development angle is always something to keep in mind when we visualize implementation of educational technology, and you raise some excellent questions. There do seem to be assumptions that the technology will be implemented smoothly (as is often the assumption), but of course we know that not all deployment is equal. It sometimes takes a rigorous training program to produce positive results. Professional development program can even harm achievement if implemented improperly.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
I am a strong believer that professional development courses and conferences are not enough. Teachers are uncomfortable with changing their methods of teaching, not usually because they are lazy or think it will not work better, but because they are nervous that they cannot handle the technology when it is used in the classroom setting.
I know when I taught English I started to use blogs with my 8th graders. When I introduced this to them I got questions about the activity itself and the technology. I was trying to troubleshoot and teach at the same time. Had I had a coach or another co-teacher in the room with me, I feel it would have gone much smoother and would have been less stressful on me when I had 30 or more kids staring at me 5 times in a day. That is why I became a technology coach, so I could help others make that leap.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
This question concerns me. I work in a high achieving school where students are stressed and overwork themselves. The competition to be the best student or have the highest GPA is fierce. While I agree that there should be access for students to continue learning outside of school, I worry that this is a push that can become unhealthy.
Recently, we have had a number of snow days. Even though these days will be made up and no time will be lost for classroom instruction in the long run, there are teachers who are pushing out learning assignments to students while they are at home. We even had some students who had school work over the one week holiday break! That seems excessive.
The ability to learn remotely should not pressure students to ignore other important aspects of their lives. Learning on the go or outside the classroom is a great thing, but I think some real conversations need to happen to ensure the push is a healthy one for k-12 students. Higher education is a different can of worms, and those people are adults so this statement is not really aimed at higher education.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
Very interesting perspective! I think anyone who has taught has seen that communication technology definitely breaks down the barriers between you and your students, enabling more frequent communication, but that also creates more opportunities to do work outside of the classroom, which comes into play in a environment like your school.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
Ashley, you make a great point about the pressure students encounter and the very real need for a conversation to take place. My son is in an international baccalaureate program as a h.s. junior and his teachers all send assignments on snow-days and he had projects assigned during the December holiday break. Of the 10 days off school, 6 of them he was studying. As a parent, I receive a copy of the emails and texts and I couldn’t believe my high school child had more homework than me during the break.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment
General Document Comments 0


For this week, please look for a segment in each text where you can reply to the following:
What does this framework for using technology in education assume about teachers and teaching?
What does this framework for using technology in education assume about students and learning?
Please offer at least one comment related to the assumptions about teaching, as well as at least one comment on each document related to the assumptions about learning (2 initial comments). Then, please reply to at least two different classmates on one of their comments (2 responses).
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment Hide Thread Detail
I din’t see the rules for engagement until the end. Apparently we all pushed your comments to the bottom. IN the future I will look for this first.
New Conversation
Hide Full Comment